When we were first introduced to GY6 engine scooters, many of us may have been unfamiliar with the workings of a carburetor and unable to make adjustments to the idle speed. At Got Scooters, our primary goal is to create a platform for individuals to communicate and gain an understanding of the fundamentals of scooters, with the intent of enhancing motorcycle knowledge for all.
If you’re into scooters and motorcycles, having some engine knowledge is essential. In this article, we’ll cover the basics of GY6 engines. Although experienced riders might find this knowledge too elementary, it can be helpful for those who are new to the world of motorcycles.
1. GY6 Engine basics
- What is GY6 Engine?
- GY6 Engine structure.
- Are all GY6 engines the same?
- GY6 vs GY7 engine.
2. GY6 Gas Scooter Carburetor Basics
- What is the carburetor?
- 150cc scooter carburetor diagram.
- How to adjust a carburetor?
- How to maintain a carburetor?
3. GY6 Gas Scooter Crankcase Basics
- What is a crankcase?
- Main Parts In GY6 Engine Right crankcase
- Main Parts In GY6 Engine LEFT crankcase
4. GY6 Gas Scooter Cylinder Head Basics
- Main Parts in the Valve System
- How does the GY6 Valve System Work
5. GY6 Gas Scooter Valve System
6. GY6 Gas Scooter Piston Basics
7. GY6 Scooter Cooling Fan
- What is the difference between forced air and air cooling?
8. GY6 Gas Scooter Electrical & Ignition System
- Electrical System
- Ignition Timing
9. GY6 Drive Train
- The basic principle of a pulley-based CVT system
- How does a scooter CVT work?
10. GY6 Final Drive
11. GY6 Start System
- Kick Start
- Electric start
Let’s go!
1. GY6 Engine Basics
WHAT IS GY6 ENGINE?
Specifically, we’ll delve into the GY6 engine, which is a small two/four-stroke internal combustion engine that’s often used in various small vehicles, such as scooters, ATVs, go-karts, and even small cars. This engine has become quite popular due to its compact size, high efficiency, and reliability. We’ll take a closer look at the GY6 engine, including its design, performance, and applications.
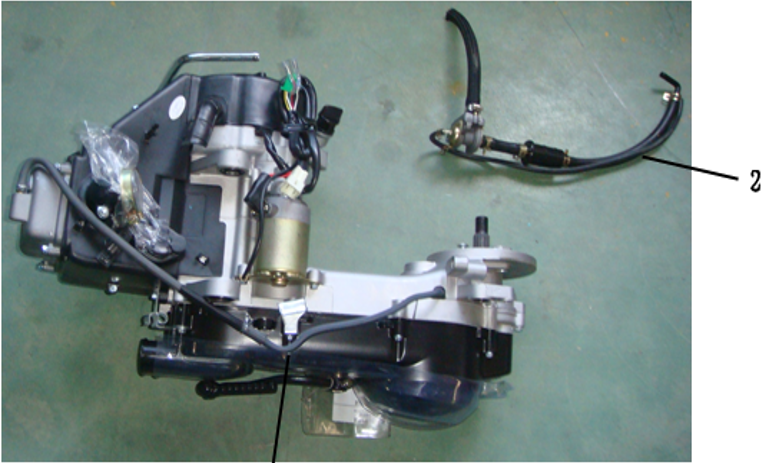
1. GY6150 short case 2. Combination valve assembly
Honda invented the GY6 engine in the 1980s, it has a displacement of 125cc, a single-cylinder air-cooled two-valve engine, a bore*stroke of 52.4×57.9 (mm), and a compression ratio of 9.2:1. In a later time, Taiwan’s Kwang Yang Motor Co., Ltd. (KYMCO) modified it and made it a standard engine.
One of the unique characteristics of the GY6 engine is its horizontal orientation, which makes it easy to mount in various small vehicles. The engine usually employs air cooling and operates its valves using a chain-driven overhead camshaft. A small timing chain powers the camshaft, which a hydraulic tensioner ensures is tight.
The GY6 engine is also notable for its continuously variable transmission (CVT). This transmission type removes the need for gears, making acceleration smooth and efficient. Instead, a system of belts and pulleys is utilized to adjust the engine-to-wheels ratio. This makes it an excellent option for adult scooters, especially for newbies. We shall delve more into CVT later.
The GY6 engine is loved for its reliability and ease of maintenance. The engine’s design is relatively simple, with most of its parts easily accessible and replaceable without special equipment. As a result, it is well-liked among DIY enthusiasts and small vehicle manufacturers.
The engine comes in variations from GY6 50cc to GY6 300cc, producing 3-14 horsepower. Its top speed is between 30 and 70 mph, depending on the tuning and displacement. This makes it an ideal option for urban environments. It has since been produced by various manufacturers in China and Taiwan, including Zongshen, Loncin, Znen, Lifan, among others.
GY6 Engine structure
Simply put, the GY6 engine system usually consists of a carburetor, crankcase, cylinder head & Cylinder Block, Valves, piston, Crankshaft, cooling fan, and drivetrain.
Sounds too complicated? Don’t worry, we will explain them one by one in the following chapters.
Before that, if you want a basic understanding of the GY6 engine structure, you can look at GY6 50cc engine diagram and GY6 150cc engine diagram. They might differ from yours in detail, but the structures are the same. You can go to Download–Service Parts.
Are all GY6 engines the same?
It’s important to note that not all GY6 engines are the same. While they are commonly used in scooters and can be either two-stroke or four-stroke, there can be differences in design, size, and performance. It’s possible that certain parts may not be interchangeable between different models of GY6 engines.
The fundamental design of a GY6 engine is a single-cylinder, air-cooled four-stroke engine with a displacement ranging from 50cc to 150cc. There might be differences in the bore and stroke, cylinder head design, carburetor type, ignition system, and other factors that can affect the engine’s performance and reliability. Nonetheless, the parameters of 125cc GY6 engines are almost fixed: bore 52.4 mm, compression ratio 9.2:1. If an engine’s bore is 52.4 mm, it’s more or less related to GY6.
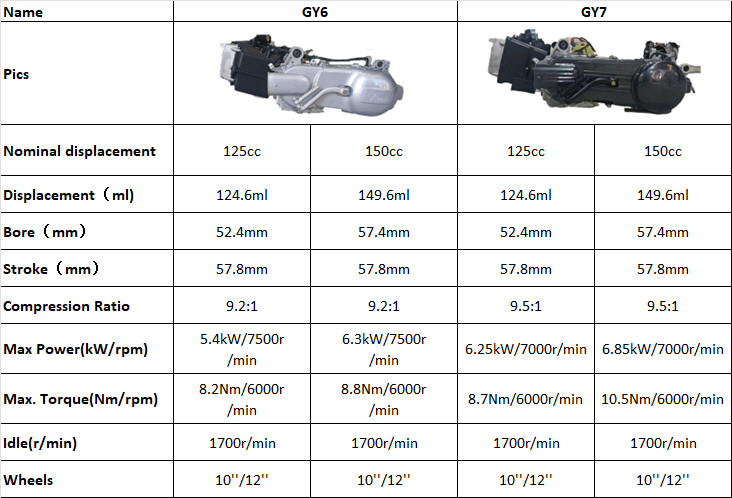
GY6 vs. GY7 engine.
What is a GY7 engine? Technically, there is no such thing as called “GY7” engine. It is an upgrade of the GY6 engine and is manufactured by some Chinese manufacturers, such as Znen (Taizhou Zhongneng Vehicle Group CO., Ltd). This modified engine is referred to as a GY7 to distinguish it in terms of power and performance.
Freedom Veracruz scooter uses a GY7 engine for a better performance.
Look at the comparison below. GY6 and GY7 engines are very similar. The difference is mainly from max power and torque.
2. GY6 Gas Scooter Carburetor Basics
What is the carburetor?
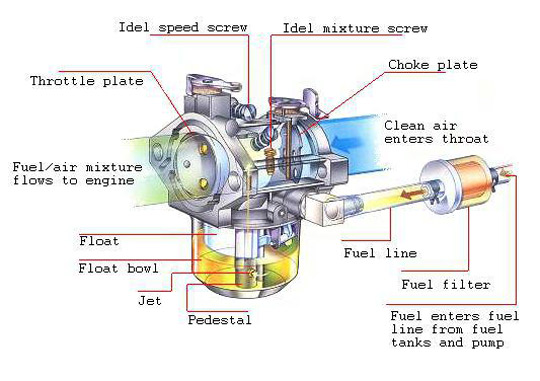
A carburetor is an important device that mixes air and fuel in the correct proportion to supply an internal combustion engine with the fuel it needs to run. Although carburetors were commonly used in entry-level 50cc to 250cc adult gas scooters, they are now less common in modern vehicles that use electronic fuel injection (EFI) systems.
For example, Freedom Canoe 50cc is an entry-level adult gas scooter. It uses a carburetor and has impressive fuel efficiency, so it is very beginner friendly. Also, in most states, driving a 50cc scooter does not require a license & insurance. The Freedom 50cc carburetor scooter is widely available in the USA, and Concept Motors in Wisconsin has a large inventory for nationwide shipping.
What does a carburetor do?
The carburetor operates using a venturi, which is a narrow section of the carburetor that speeds up the air and reduces its pressure, resulting in a vacuum. The vacuum then pulls fuel through a small nozzle and mixes it with the air in the venturi to create a combustible mixture. This mixture is then transported to the engine through a series of pipes or hoses, where it is ignited to generate power. Watch the video below for a better understanding of the principle and process.
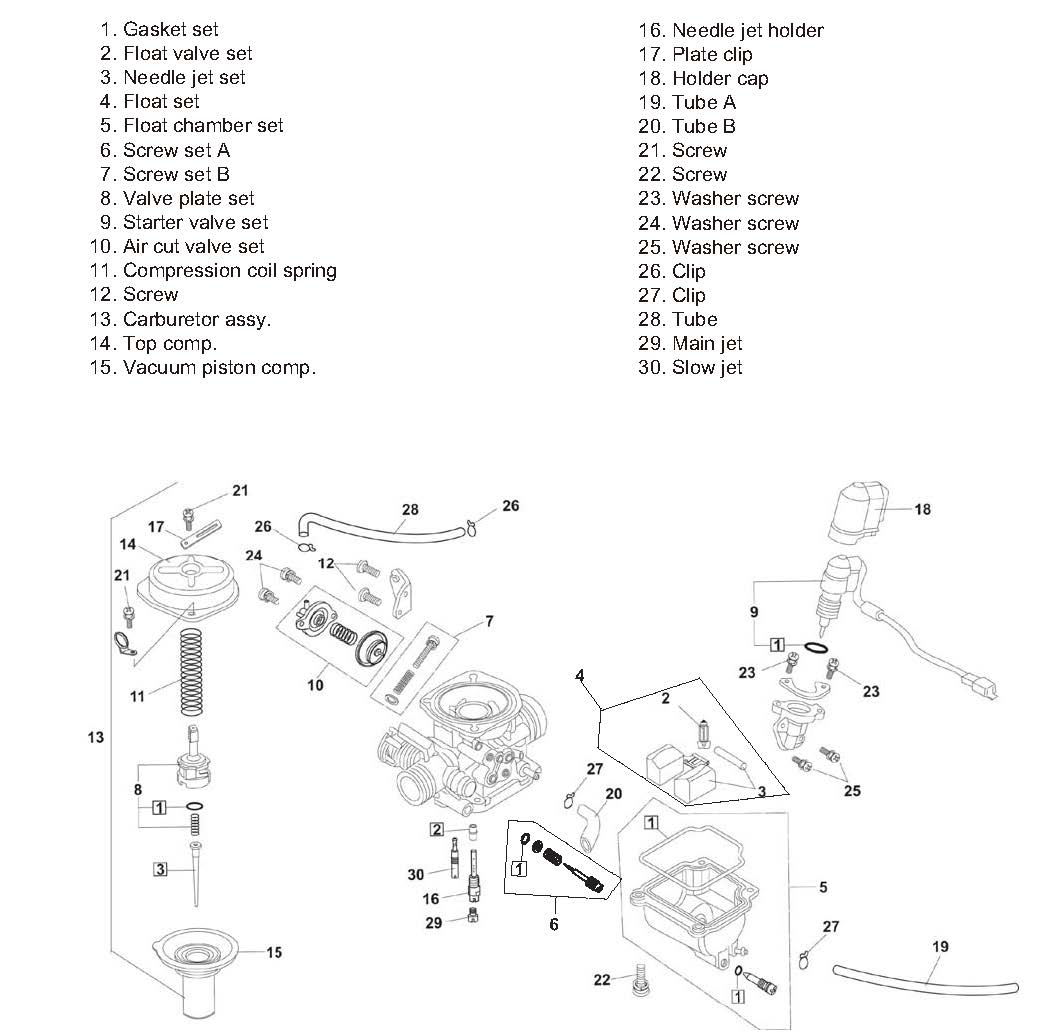
The main parts of the carburetor:
- Air intake: This is the opening through which air enters the carburetor.
- Throttle valve: This controls the amount of air that enters the carburetor.
- Fuel bowl: This is where the fuel is stored before being drawn into the carburetor.
- Float: This regulates the fuel level in the fuel bowl.
- Needle valve: This controls the amount of fuel that enters the carburetor.
- Venturi: This constricted section of the carburetor creates a low-pressure area, which draws in fuel.
- Jet: This regulates the amount of fuel that enters the carburetor.
- Choke: This restricts the amount of air that enters the carburetor, creating a richer fuel mixture for starting the engine in cold conditions.
- Accelerator pump: This provides a shot of extra fuel when the throttle is opened rapidly, such as during acceleration.
- Idle adjustment screw: This controls the engine’s idle speed by adjusting the amount of air that enters the carburetor at idle.
GY6 150cc scooter carburetor demo diagram.
Cross section Diagram
How to adjust a scooter carburetor?
Since the idle speed adjustment screw greatly influences the engine’s performance, the carburetor’s idle speed adjustment screw has been strictly tested and adjusted to the best position before leaving the factory.
Generally speaking, users without experience are not suggested to adjust the idle speed adjustment screw alone. However, if the position of the idle speed adjustment screw does change after a long period of use, it should be adjusted.
- Warm up the engine: Start and let it run for a few minutes to warm up.
- Locate the carburetor: On most scooters and ATVs, the carburetor is located on the top of the engine.
- Adjust the air screw: Use a small screwdriver to turn the air screw. Start by turning the screw clockwise until it is lightly seated, then turn it counterclockwise for 1-2 turns. This is a good starting point for most engines.
- Adjust the idle speed: Use the idle speed screw to adjust the engine’s idle speed to the manufacturer’s specifications. This may be listed in your engine’s owner or service manual. Usually, you should maintain it around 1500 RPM for scooters.
- If you cannot find the screws, refer to the “Cross section Diagram “picture above or consult your dealers.
- Fine-tune the air screw: Turn the air screw in small increments (usually 1/8 or 1/4 turn at a time) until the engine reaches top RPM and has a steady running, then fine-tune the idle speed screw again around 1,500 RPM (or match MFR specs). Adjust the idle speed screw to restore to the correct specification if the engine idle speed increases or decreases.
- Check the throttle response: Once you’ve found the optimal setting for the air screw, test the engine’s throttle response. Quickly open the throttle and let it snap shut. The engine should return to a smooth and steady idle. If the engine stumbles or dies, adjust the air screw again in small increments until the throttle response is smooth.
How to maintain a SCOOTER carburetor?
Maintaining a GY6 carburetor is essential to keep your scooter or motorcycle running smoothly. Here are some tips for maintaining a GY6 carburetor:
- Regular cleaning: Clean the carburetor regularly to remove any dirt, debris, or buildup that can clog the jets or cause other issues. You can use carburetor cleaner or compressed air to clean the carburetor.
- Regularly check whether the connection of the carburetor, intake pipe, intake valve and crankcase intake is tight and firm. Otherwise, it will leak air due to looseness, and the mixture will become thinner, resulting in difficulty starting the engine or poor operation.
- Check the air filter: Make sure the air filter is clean and functioning correctly. A dirty air filter can cause the carburetor to run lean or rich, leading to poor performance and fuel economy.
- Check the fuel filter: Make sure the fuel filter is clean and not clogged. A clogged fuel filter can restrict fuel flow to the carburetor.
- Check the fuel lines: Inspect the fuel lines for any signs of damage or cracks. If you notice any damage, replace the fuel lines.
- Adjust the idle speed: Adjust the idle speed as needed. A low idle speed can cause stalling, while a high idle speed can lead to overheating and increased wear on engine components.
- Adjust the air/fuel mixture: Adjust the air/fuel mixture screw to optimize performance and fuel economy.
- Use high-quality fuel: Use high-quality fuel to prevent contamination and buildup in the carburetor. Avoid using old or stale fuel, as this can cause carburetor problems.
Tearing down and cleaning a carburetor generally requires more expertise, so we suggest you go to a dealer shop for assistance or buy a new one, as the price is very affordable. It usually takes around $30 shipped. If you wish to know more about cleaning the carburetor, here is a video you can learn from:
3. GY6 Gas Scooter Crankcase basics
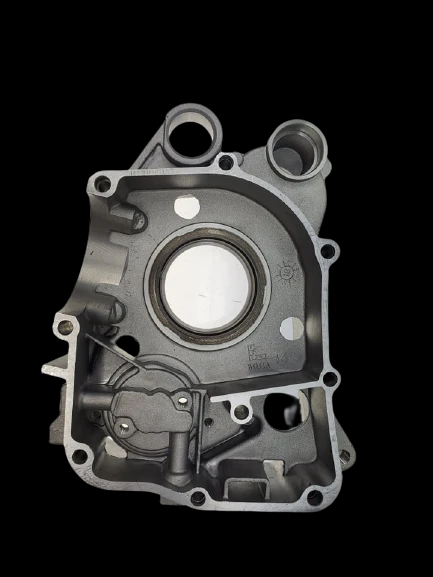
What is a Crankcase?
A GY6 engine crankcase is part of a GY6 engine that seals and supports the engine’s Crankshaft and other related components. The crankcase is the lower part of the engine block, and it is typically made of aluminum or other lightweight materials.
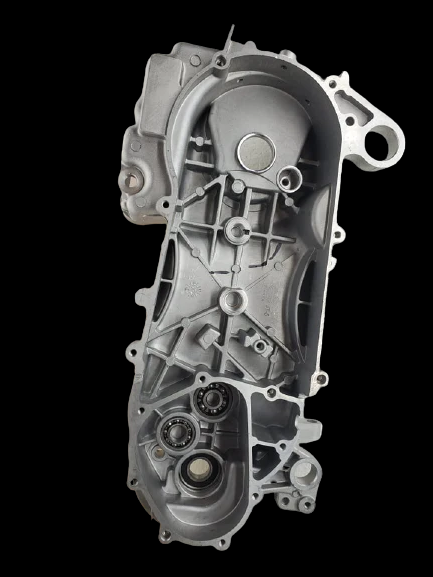

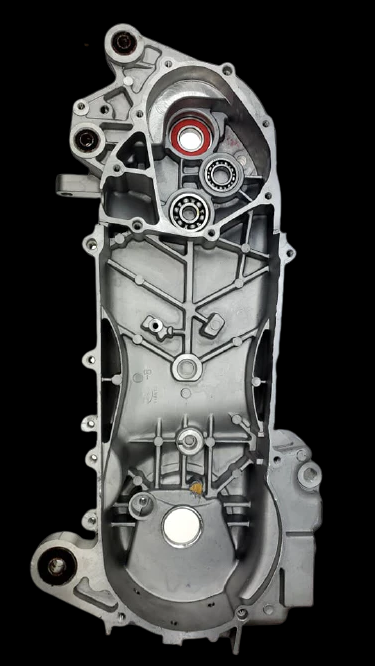

Main Parts In GY6 Engine Right Crankcase:
Magneto: It generates electrical power to charge the battery and power the engine’s ignition system and other electrical components.
Gears Train: A set of gears that transmit power from the clutch housing to the rear wheel.
Clutch Assembly: A device that connects and disconnects the engine from the transmission.

Oil Pump: A pump that circulates engine oil through the engine to lubricate moving parts and reduce friction and wear.
Main Parts In GY6 Engine Left crankcase:
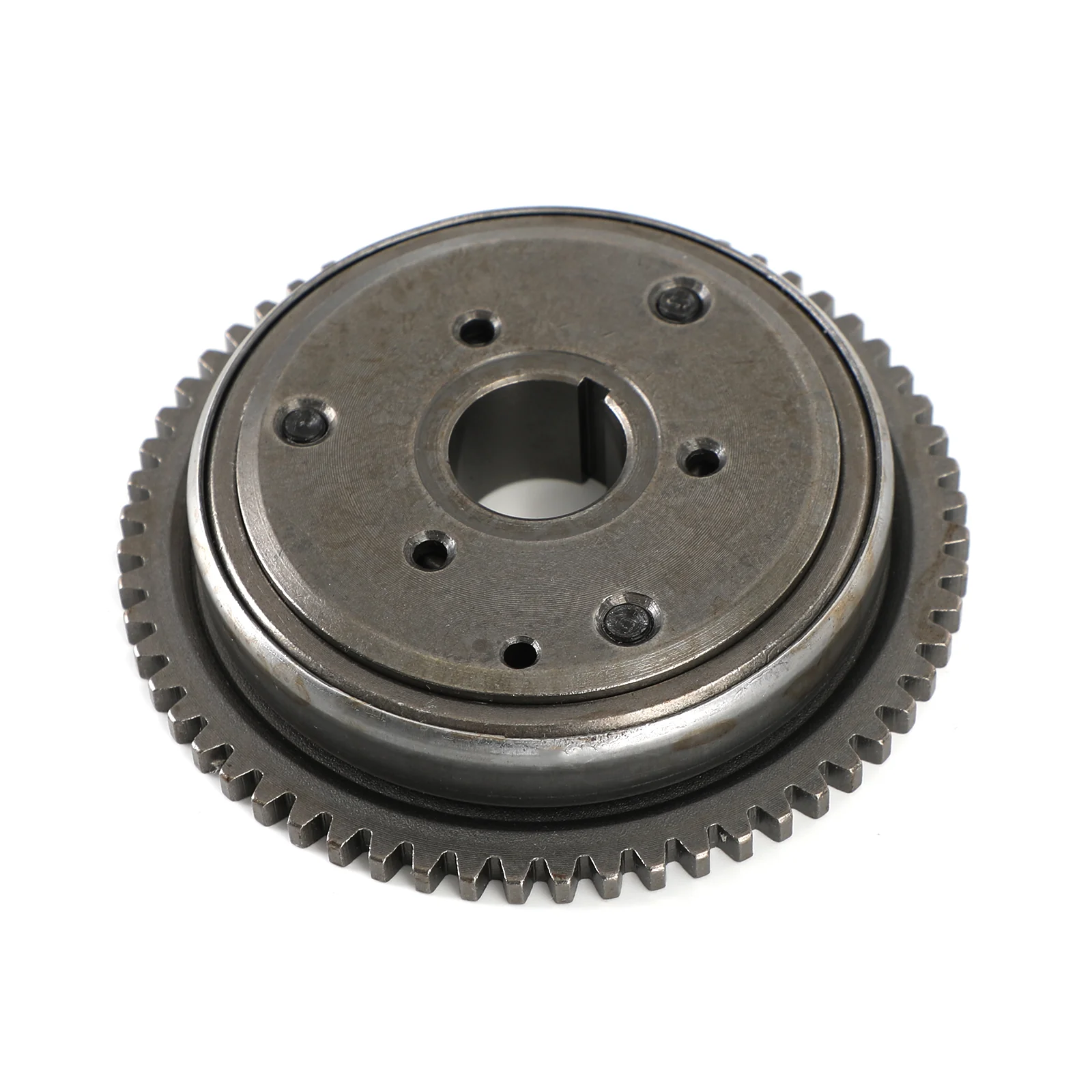
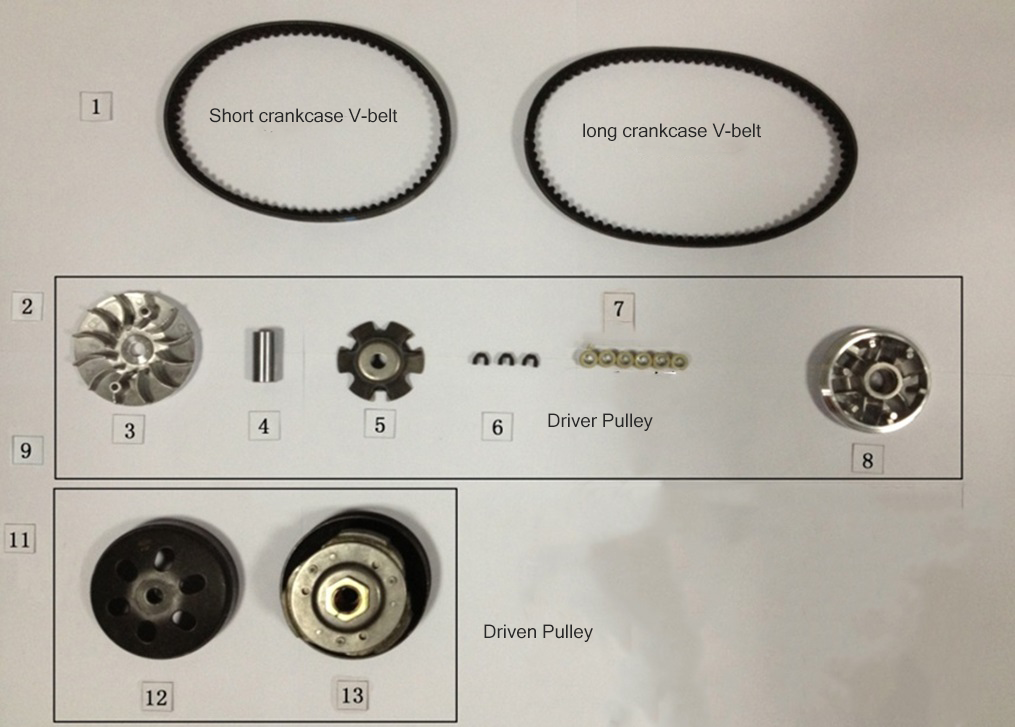
Driver Pulley: The driver pulley, also known as the “Variator,” is attached to the engine crankshaft and is responsible for transmitting power through the V-belt to the driven pulley.
V-belt: The V-belt connects the driver pulley to the driven pulley in the CVT system. As the driver pulley rotates and expands due to centrifugal force, the V-belt is forced to ride higher on the driver pulley and lower on the driven pulley. This changes the effective gear ratio and allows the engine to maintain a constant RPM while accelerating.
Driven Pulley: The driven pulley is attached to the transmission input shaft and transmits power to the output gears.
Kick Starter: A lever-operated mechanism that can be used to manually start the engine in case of a dead battery or other issues.
How to tell if a crankcase is good?
It should have good airtight performance, smooth and flat, and clear outline, using high precision parts, thereby reducing engine noise and increasing durability.
4. GY6 Gas Scooter Cylinder Head Basics
The cylinder head is comprised of the cylinder head cover and the cylinder head itself. The spark plug and exhaust pipe are visible on the exterior of the cylinder head, while the carburetor allows the combustible mixture gas to enter the combustion chamber through intake pipes that sit between the cylinder head. The interior structure of the cylinder head includes a fixed camshaft, valve rocker arm, intake and exhaust valve guides, oil seals, valve springs, and more.
Not only does the cylinder head cover act as a seal, but it also combines with the cylinder head to form the space where the gas distribution mechanism is installed.
In summary, the cylinder head has two crucial functions: regulating intake and exhaust and creating the combustion chamber in conjunction with the cylinder.


5. GY6 Gas Scooter Valve System
We know that the soul of the internal combustion engine is combustion. The best combustion requires two conditions: a suitable place and a suitable timing. Only when the timing of intake, exhaust action, and ignition are both optimal, that is, fuel timing and ignition timing! The valve train is to control the opening and closing of the valves at the right time.
Before we explain how the system works, we need to understand a few parts.
- Camshaft
- Cam
- Camshaft fixing position
- Timing chain
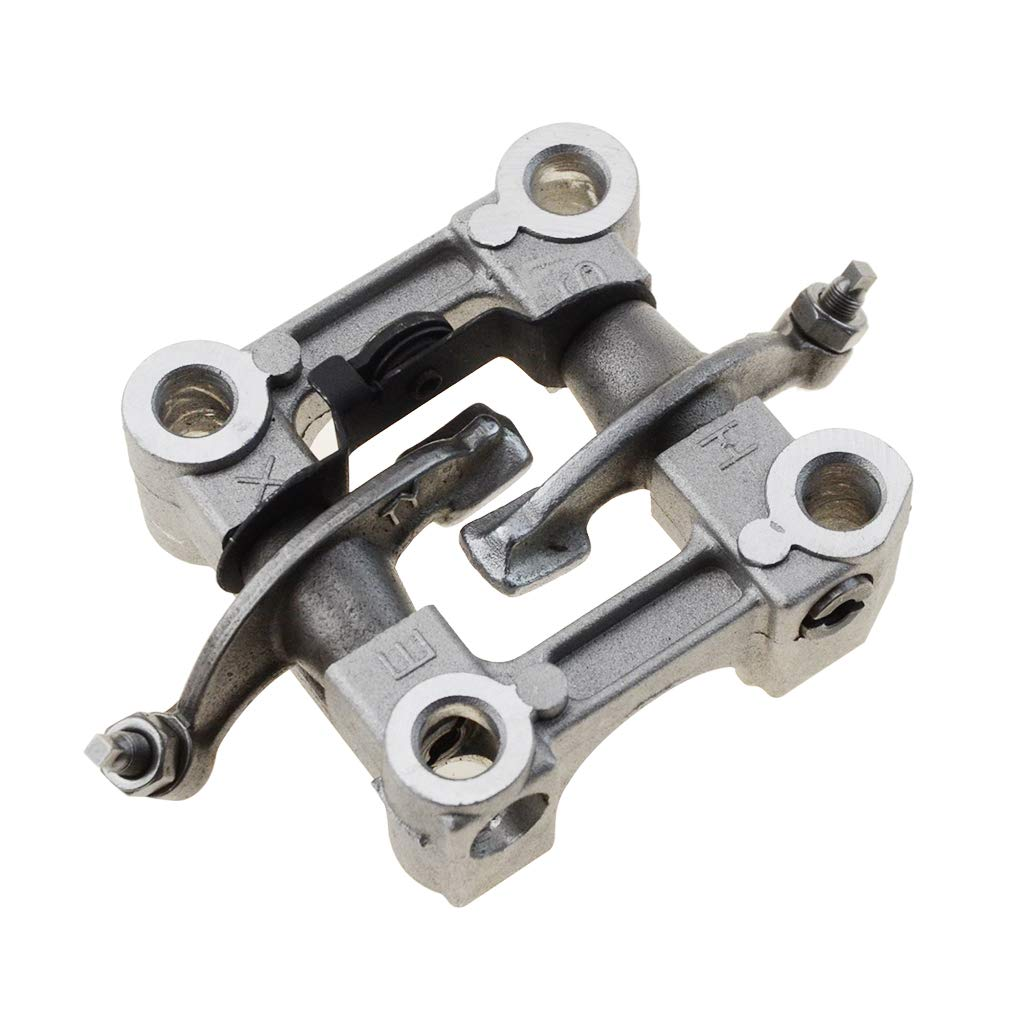
- Rocker arms
- Valve assembly
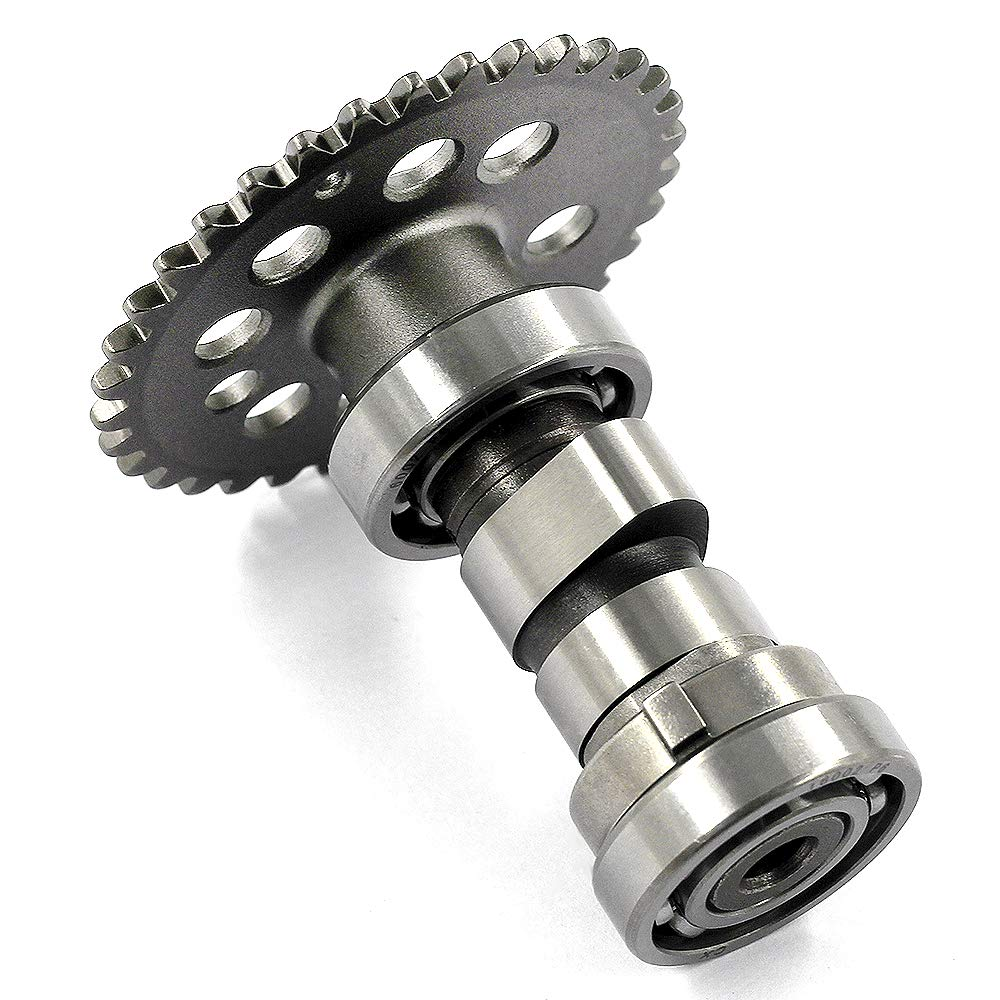


It looks like this if we put them together.
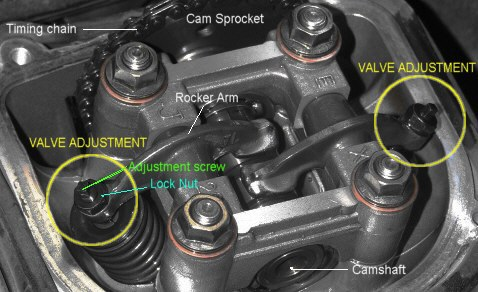
We have seen the main parts of the scooter valve system, but how do they work together?
The Crankshaft drives the camshaft to rotate through the timing chain. When the camshaft rotates to the convex part of the cam, it starts to jack up the rocker arm, so that the rocker arm swings around the rocker arm shaft and compresses the valve spring, pushing the valve down, that is, the valve opens.
When the convex part leaves the rocker arm, the valve moves upward under the force of the spring. That is, the valve is closed.
The number of gears between the crankshaft sprocket and the camshaft sprocket is 2:1, so the Crankshaft rotates twice, and the camshaft rotates one time the intake and exhaust valves open once each.
The complete cycle will be four stages:
- Air in
- Compression
- Burning
- Exhaust
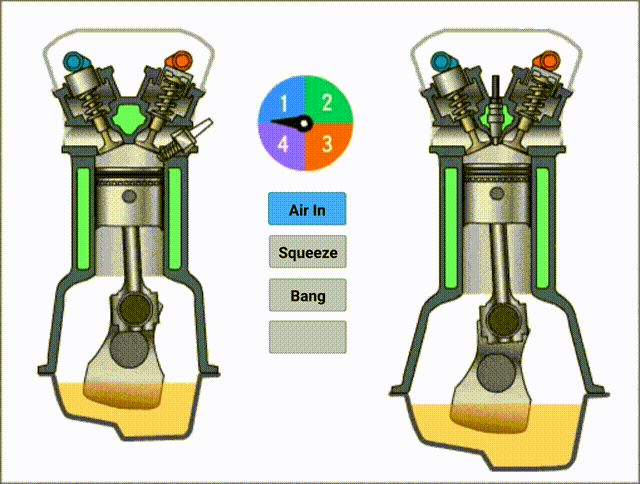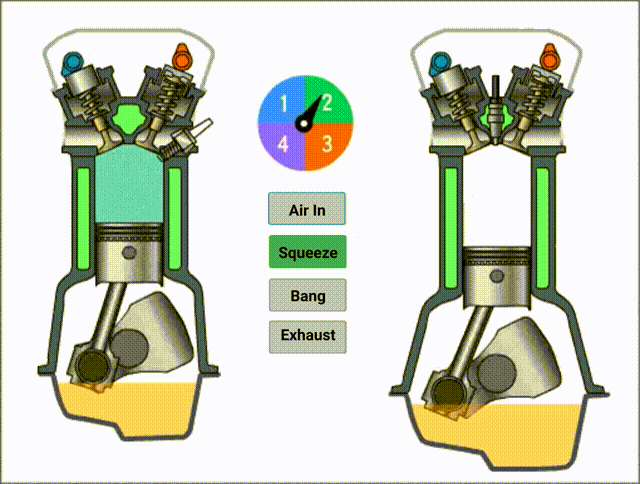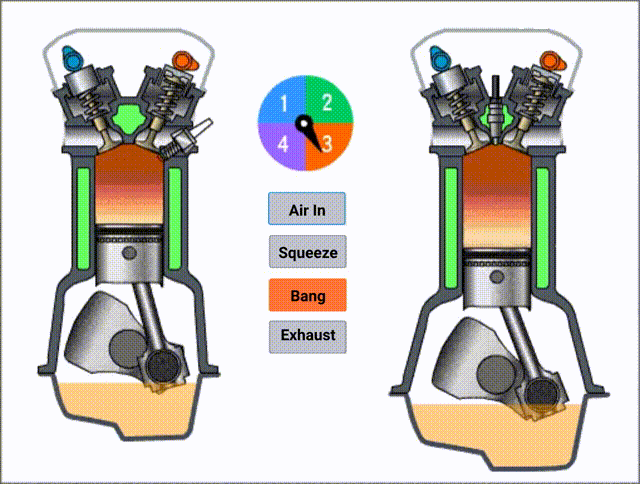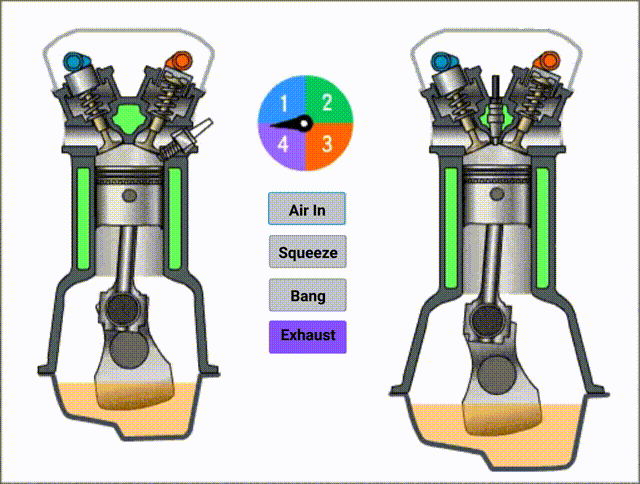
In the below picture, you can see the structure more clearly.
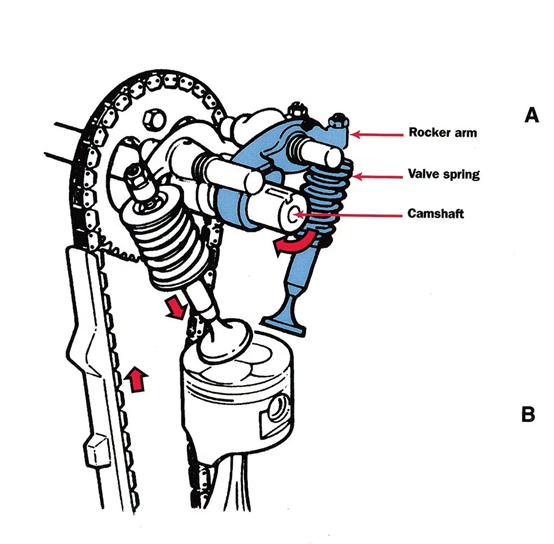
6. GY6 Gas Scooter Piston Basics
When the mixture is burned, the piston reciprocates up and down in the cylinder.
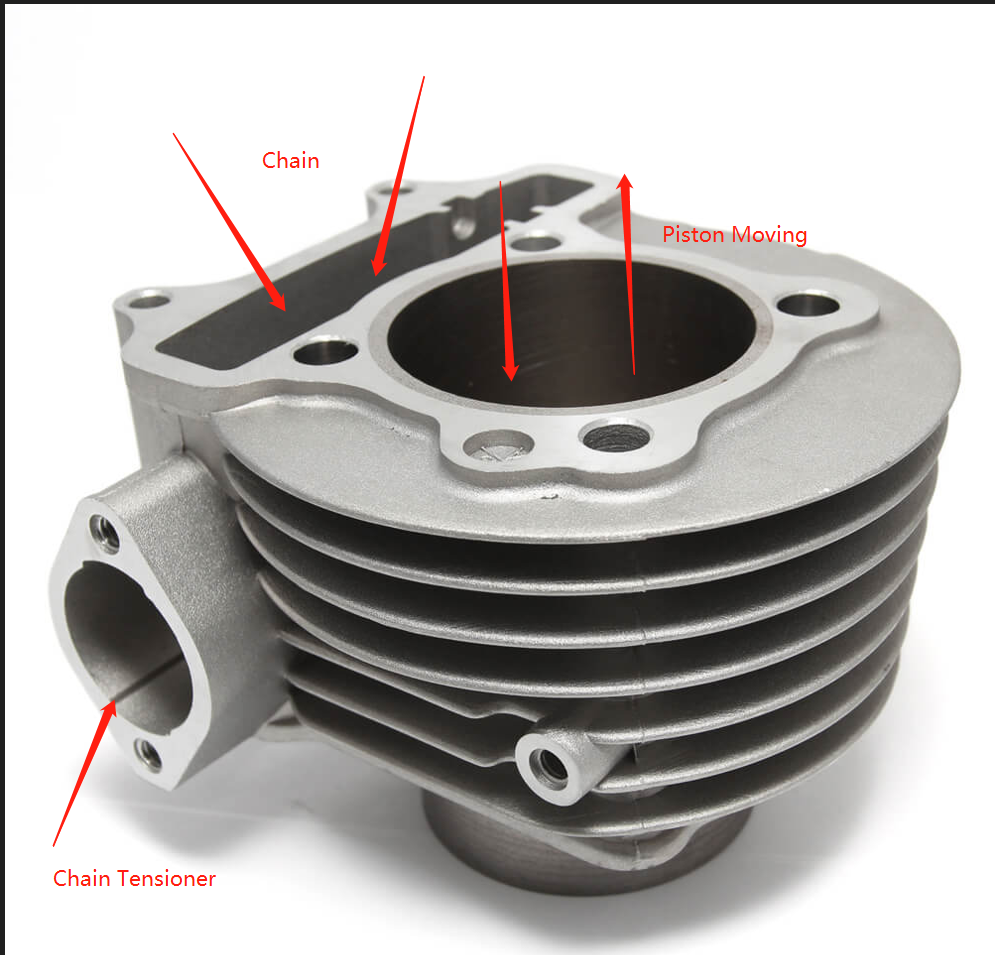
The Crankshaft connecting rod converts the piston’s up-and-down reciprocating motion into the Crankshaft’s rotational motion, which then transmits the power to the transmission mechanism to drive the rear wheel to rotate.
See the motion below:
There are ring grooves on the piston, which are used to install the piston rings. The piston ring is divided into gas ring and oil ring. Also, you will notice that there are 2 dents on the top of the piston, they are set to prevent the piston from colliding with the intake and exhaust valves when it is at the top dead point of the cylinder.
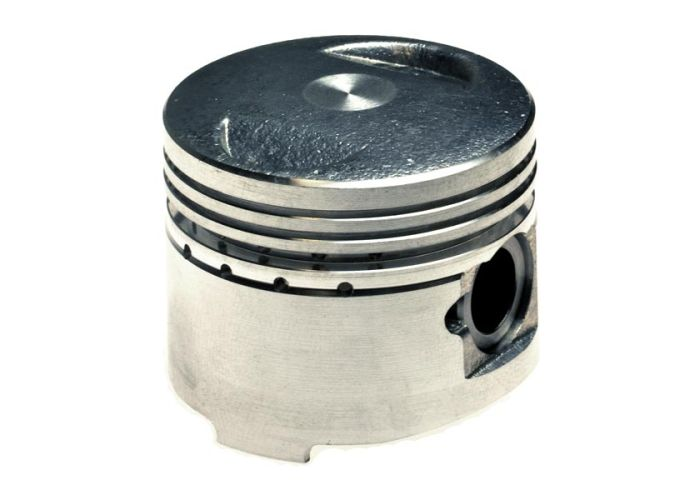

GY6 has two air rings and one oil ring. The gas ring prevents gas in the combustion chamber from entering the crankcase, while the oil ring is used to prevent lubricating oil from entering the combustion chamber.
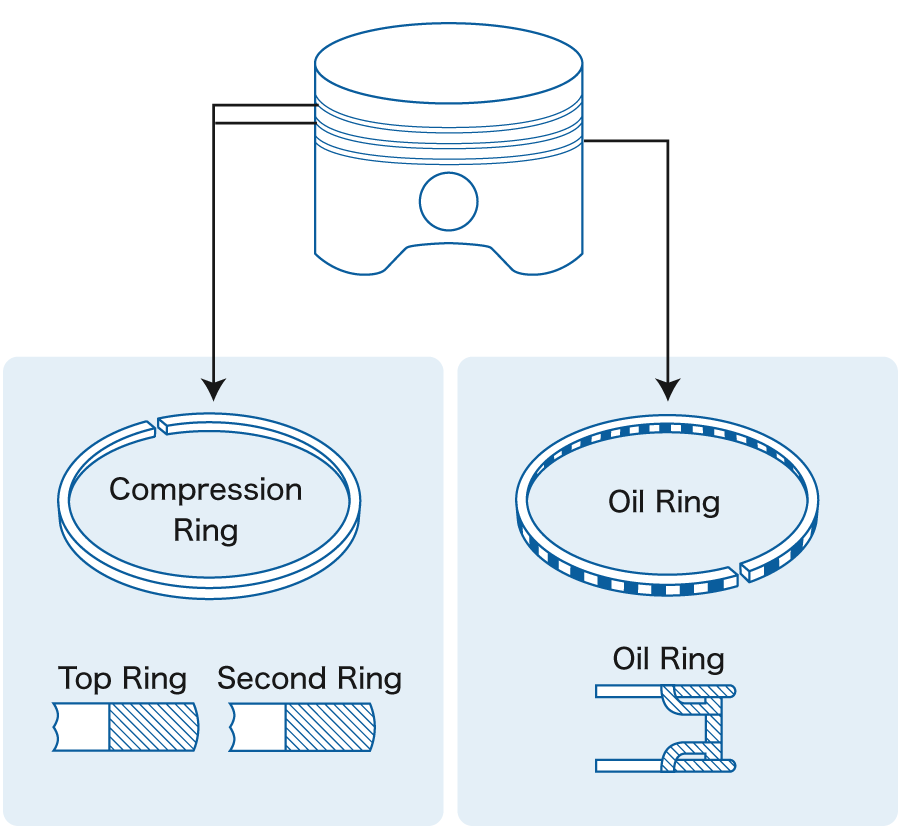
7. GY6 Scooter Cooling Fan
We often hear forced air cooling engines.
What is the difference between forced air and air cooling?
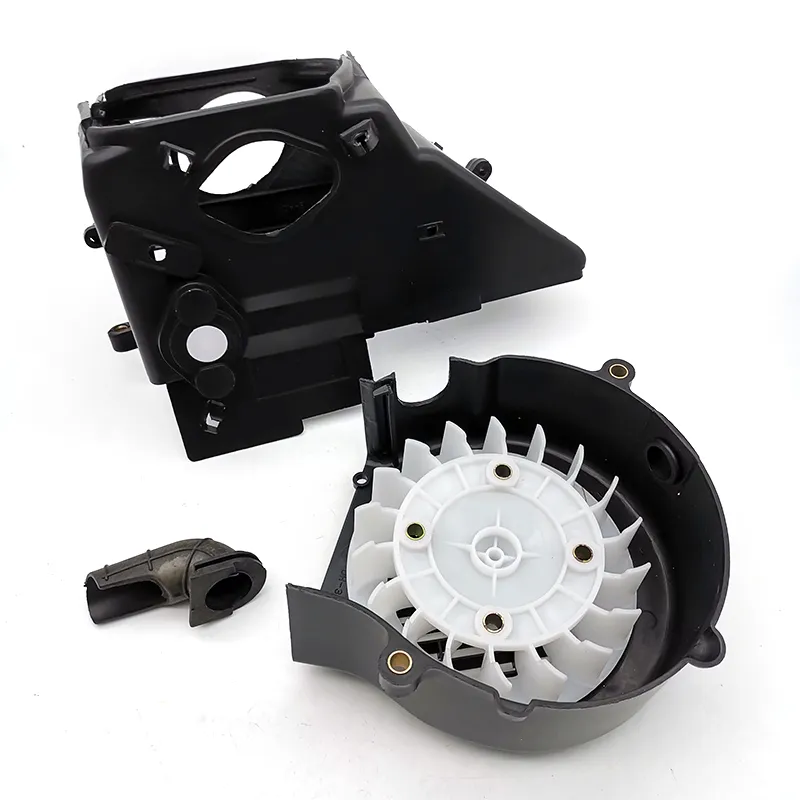
The air-cooling engines rely on air to circulate directly over the cooling fins or hot areas of the engine to cool them, keeping the engine within its operating temperature range. There are no extra fans to cool down the temperature, and it 100% relies on the wind generated while driving for cooling. It is also called driving air cooling.
While forced air cooling engine usually has cooling fans, they are located at the right side of the crankcase, the cooling fans rotate with the flywheels and cool the engine all the time (as long as the engine is on).

8. GY6 Gas Scooter Electrical & Ignition System
Electrical System
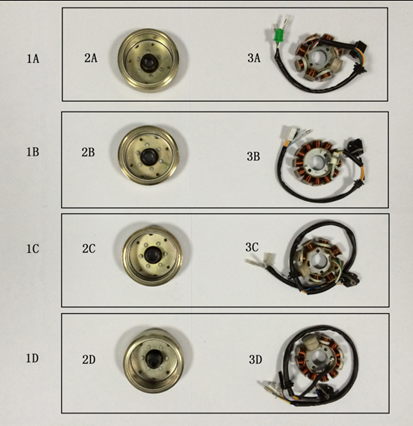
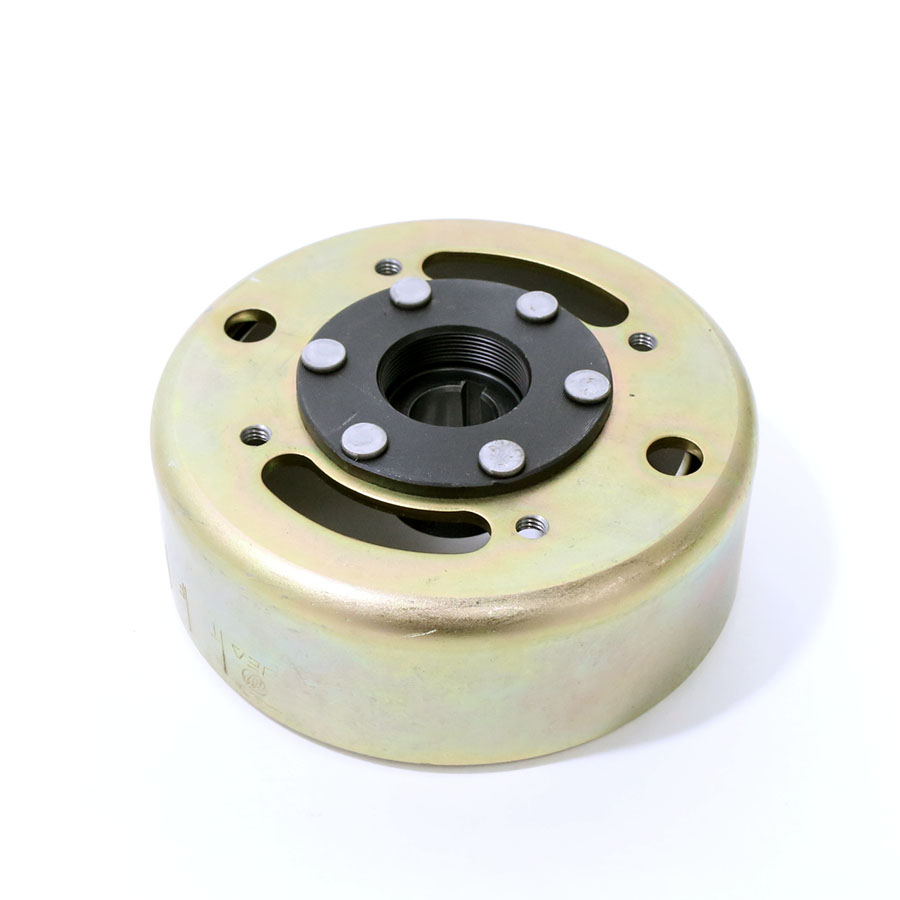
The magneto coil cuts the magnetic force lines to generate alternating current, and the generated power serves as the energy source for all vehicle electrical components. GY6 magneto comprises a flywheel assembly and a stator, it plays the role of generating electric power.
The flywheel assembly is also called the rotor assembly, and there are six permanent magnets on the inner edge of the metal shell;
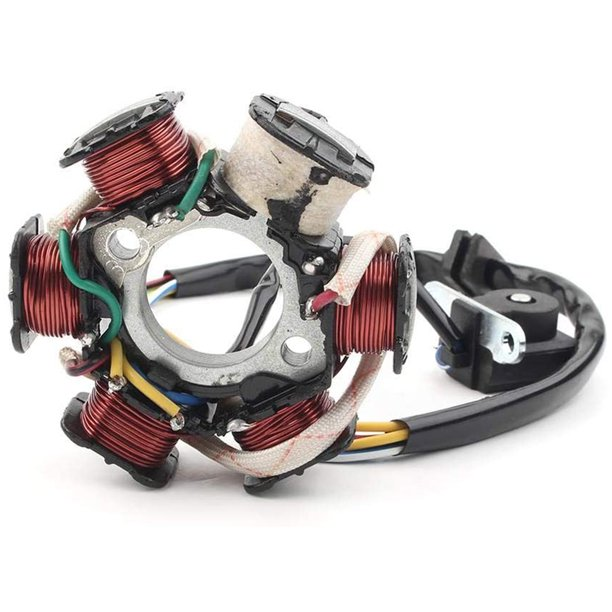


The stator is composed of 6 copper wire winding coils. The GY6 stator has three sets of independent coils:
1.. The first set charges the energy storage unit(capacitor) in the CDI igniter, and we call it a low-voltage ignition coil. The full name of CDI is Capacitor Discharge Ignition, consisting of one capacitor, one silicon-controlled rectifier, and one diode.
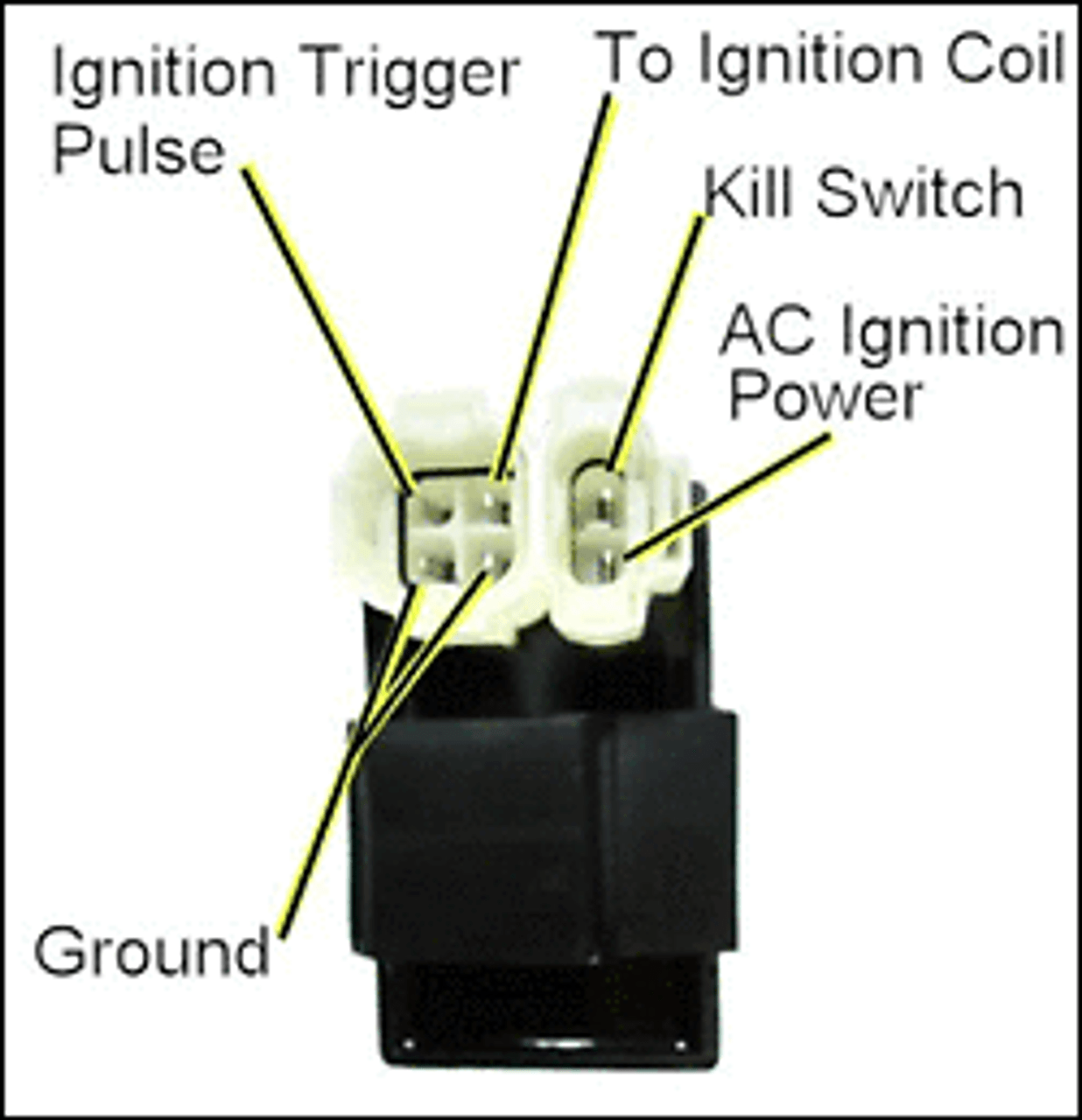
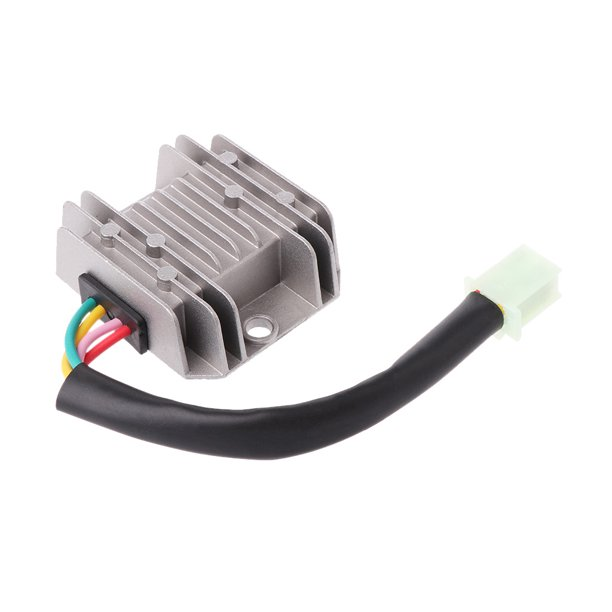
2. The second group is to charge the battery and supply the headlights, which we call the charging & lighting coil. The AC electricity from the charging & lighting coil will be adjusted to DC by the rectifier, and then it goes in two directions, one is to allow the alternator charges the battery, and the other is to supply the headlight’s power.
See the below picture of the rectifier. Inside it is a stabilized rectifier circuit board, which is potted with epoxy resin and then installed in a cast aluminum box with the heat sink.

3. The third group is the trigger coil, which controls the discharge of the capacitor in the CDI. Then the ignition coil will amplify the pulse voltage output from the CDI to generate high voltage and then pass through the high voltage line to the cap, discharging the spark plug. Usually, the high voltage of the spark discharging can reach over 10KV.
The magneto is installed on the right crankcase, you will see the flywheel after you remove the cooling fans.
Ignition Timing
Proper ignition timing is crucial for maximizing the power performance of an engine. Once the mixture is optimally compressed within the cylinder, it’s time to ignite.
The question is, when is the optimal timing? Is it when the piston moves to the top end? The answer is No. It is because the combustion of gasoline takes a certain amount of time from the beginning of combustion to the end of it, so before the piston’s compression stroke reaches the top dead of the cylinder, it needs to be ignited in advance. Usually, the advanced ignition timing is also called the ignition timing angle.
In GY6 engines, the ignition advance time is achieved by the relative position of the magneto trigger coil and the flywheel trigger magnet. There is an installation alignment mark on the right crankcase cover.
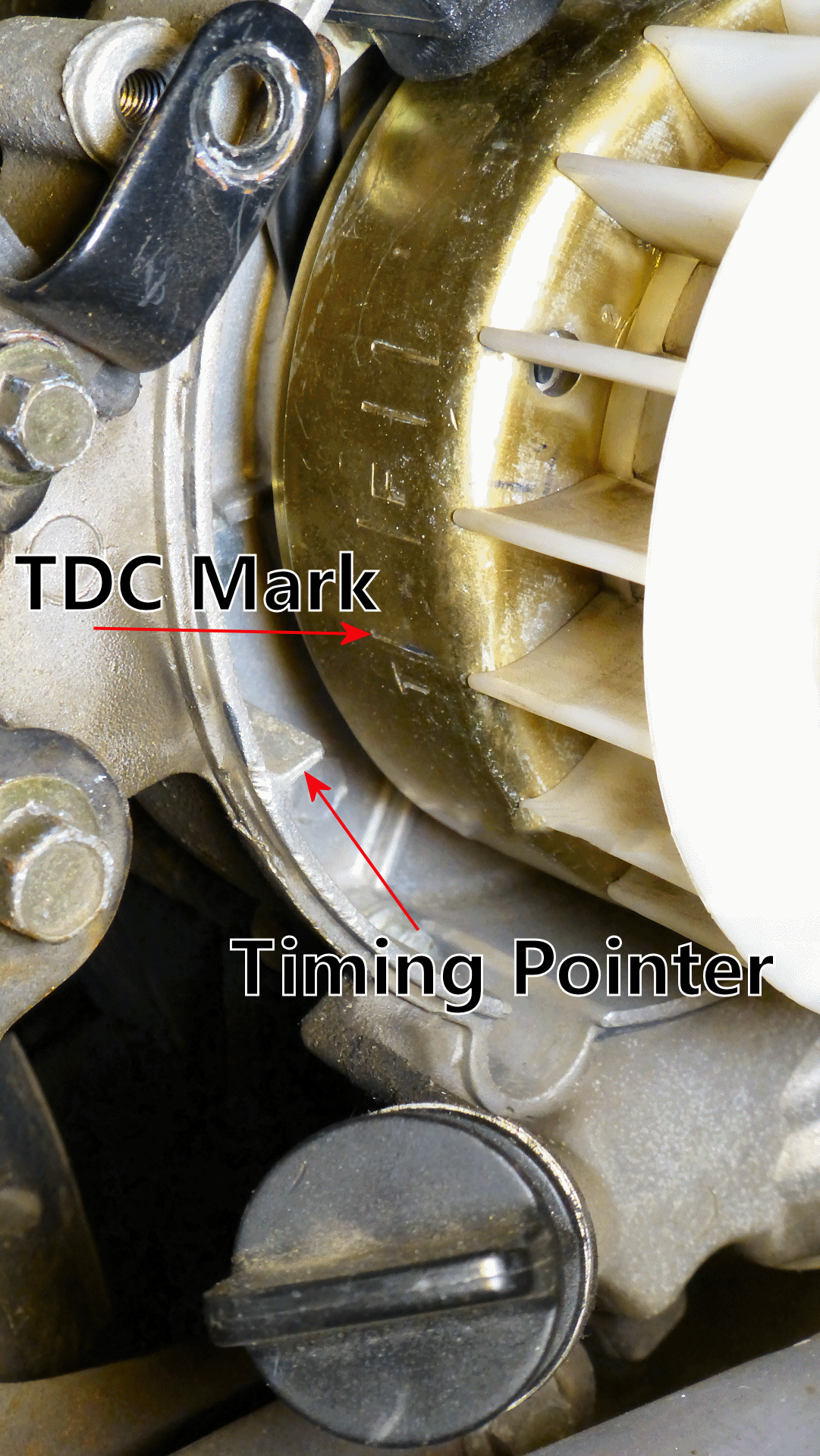
In addition, limited ignition advance angles can also be provided in CDI igniters, usually around 10 degrees. Therefore, the ignition advance angle range that GY6 can provide is relatively small. A chip can adjust the angle (timing) based on the different RPMs for advanced scooters to get the best power and torque, there is no CDI on an ECU-controlled scooter.
9. GY6 Drive Train

In our previous content, the Crankshaft connecting rod converts the up-and-down reciprocating motion of the piston into the rotational motion of the Crankshaft, but how is the power of the Crankshaft transmitted to the rear wheels?
We know that the rotation speed of the Crankshaft is very high, and the scooter starts at about 2200 rpm. Obviously, the rear wheels can’t move at such a speed. We need to obtain different speeds and torques at different speeds. The variable speed system provides this function to complete.
In addition, when we are driving, the scooters need to send power to the rear wheels, and when we want to stop, we need to be able to cut power, and the clutch does this. The clutch gently transmits power (cutting off power) between the Speed and transmission systems.
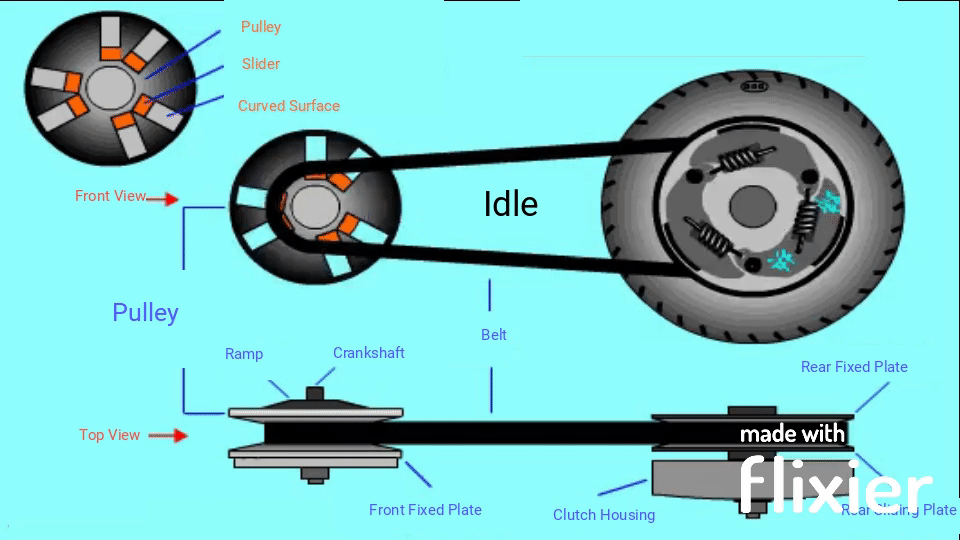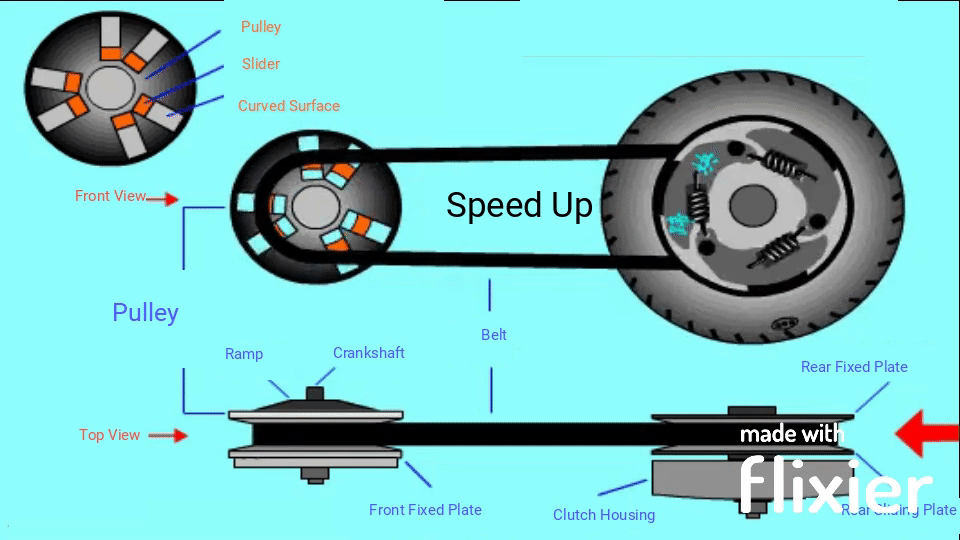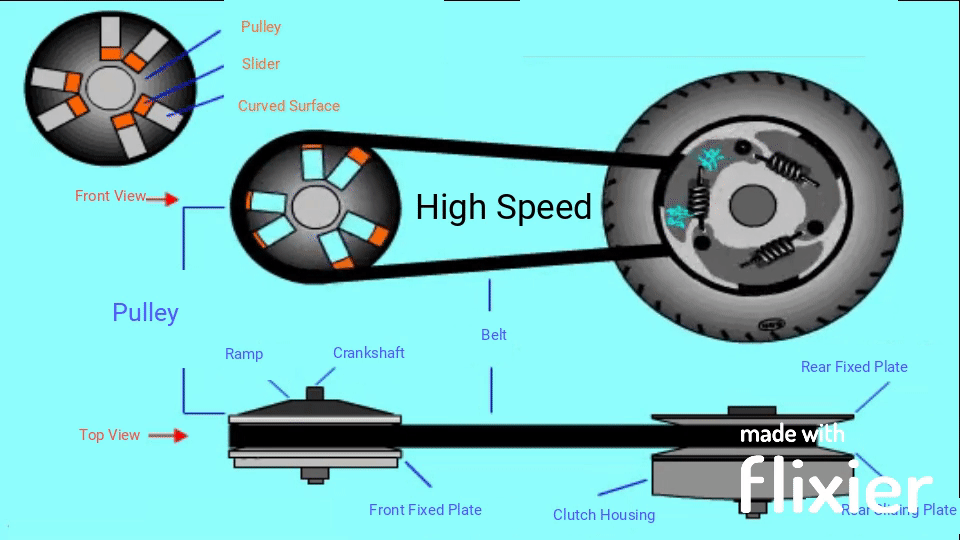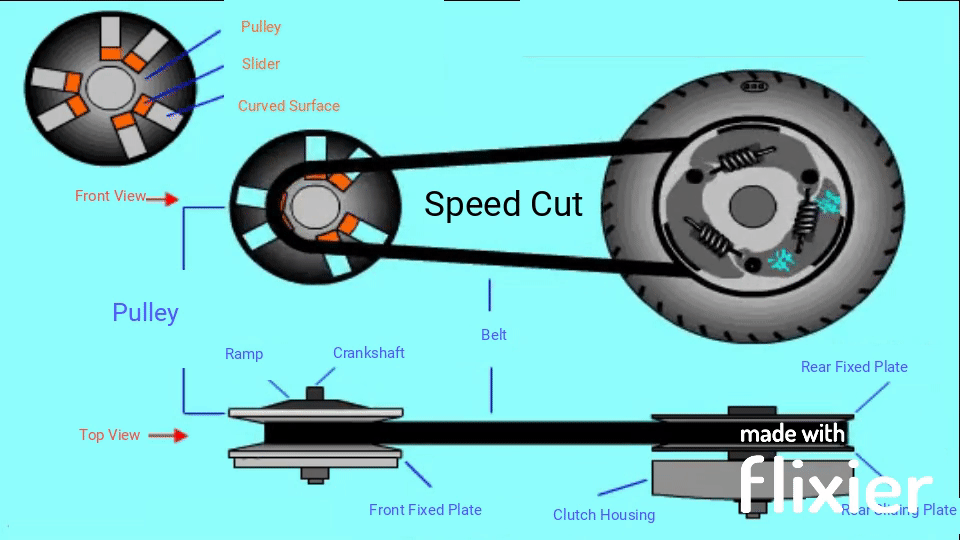
So in a word, the drive train mainly consists of the pulley, belt and clutch, in means of inertia and centrifugal force to implement continuously variable transmission (CVT).
The basic principle of a pulley-based CVT system
There are 2 pulleys in this system, the driver pulley and the driven pulley, a V-belt with constant length runs between these two pulleys. When the RPM goes up, the scooter has a higher speed, the diameter of the driver pulley increases and the driven pulley decreases the diameter; when you need to obtain the high torque, the diameter changes go opposite. However, changing the pulley’s physical diameters is impossible, so engineers develop something that can have the same effect.
Instead of changing the diameters of the pulleys, we change the diameter of the belt. When the engine runs at low RPM, the belt stays at the maximum diameter of the driven pulley to achieve high torque but low RPM; The belt diameter on the driver pulley must be increased to obtain a higher RPM.
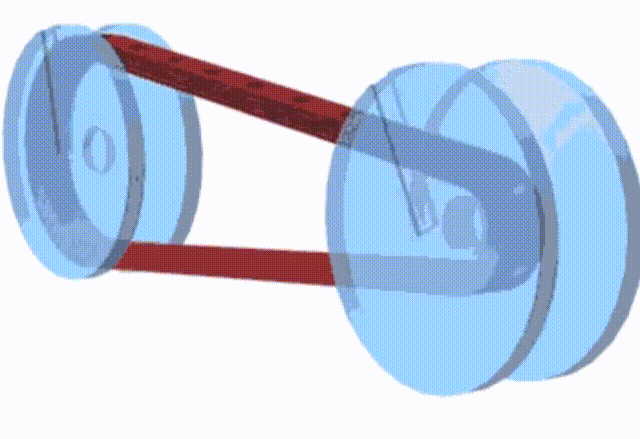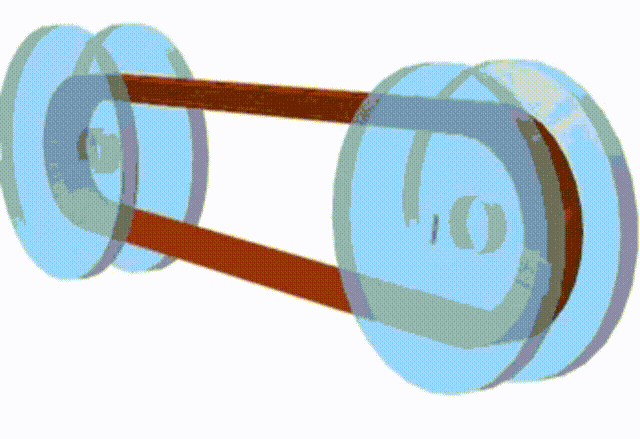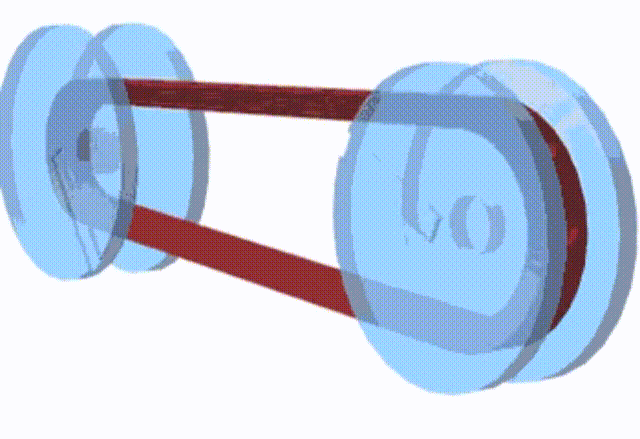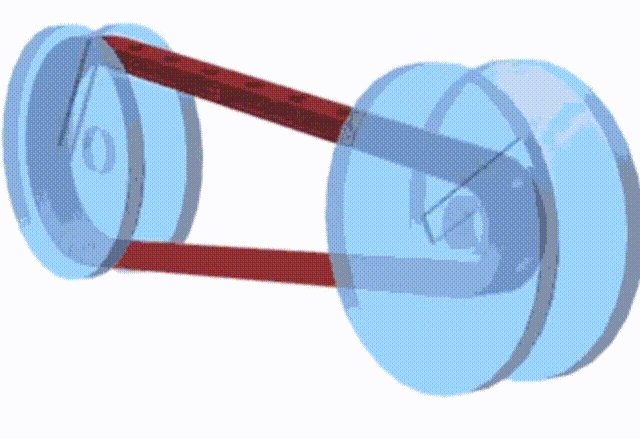
How does the GY6 Valve System Work
In the driver pulley, there are two conical plates, one is fixed with an input shaft and the other is free to slide along its axis, in the sliding conical plate, there are a set of rollers (usually six pieces), and they are the important factors to change the speed.
On the rear side, the driven pulley also has two plates and one is fixed but the other can slide, with the force of a compression spring, it makes the sliding plate of the driven pulley stay close to the other plate;
The clutch housing system is behind the driven pully, the inner structure includes weighted arms, extension springs and friction pads. These are the key factors to transmit/cut off power.
When the scooter is off or at idle speed, rollers stay in the center of the sliding plate of driver pulley, and the compression spring forces the sliding plate of driven pulley to stay close to the other plate, the belt has a bigger diameter on driven pulley, friction pads are held by the extension spring, they are not engaged with clutch housing;
When the engine moves faster, all the rollers move outwards under centrifugal force and along a curved surface, then push against the ramp plate. Since the ramp plate is fixed, the sliding plate moves towards the other plate, and it pushes the belt outwards. This action makes the belt has a bigger diameter on the driver pulley, since the belt length is constant, the diameter on the driven pulley decreases; after sufficient speed is reached, the friction pad will overcome the force of the extension spring and engage with the clutch housing, then transfer power to the rear wheel through a gear train.
Here is an animation you don’t want to miss, I cannot find anything better than this video to explain how a scooter transmission works.
10. GY6 Final Drive
The GY6 gearbox diagram shows that the gearbox is positioned at the back of the crankcase. Its purpose is to decrease the RPM for the rear wheel while increasing the torque. It’s important to consider that when the Crankshaft is operating at a high RPM, connecting it directly to the rear wheel results in high RPM but low torque, which leads to inadequate acceleration.
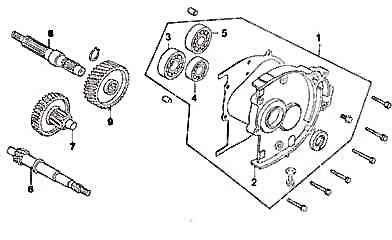
Parts 3, 4, and 5 are the bearings (6204, 6202, 6203 bearings), part 6 is the drive shaft, part 7 is the mid gear, part 8 is the output shaft (also called the countershaft), and part 9 is final gear.
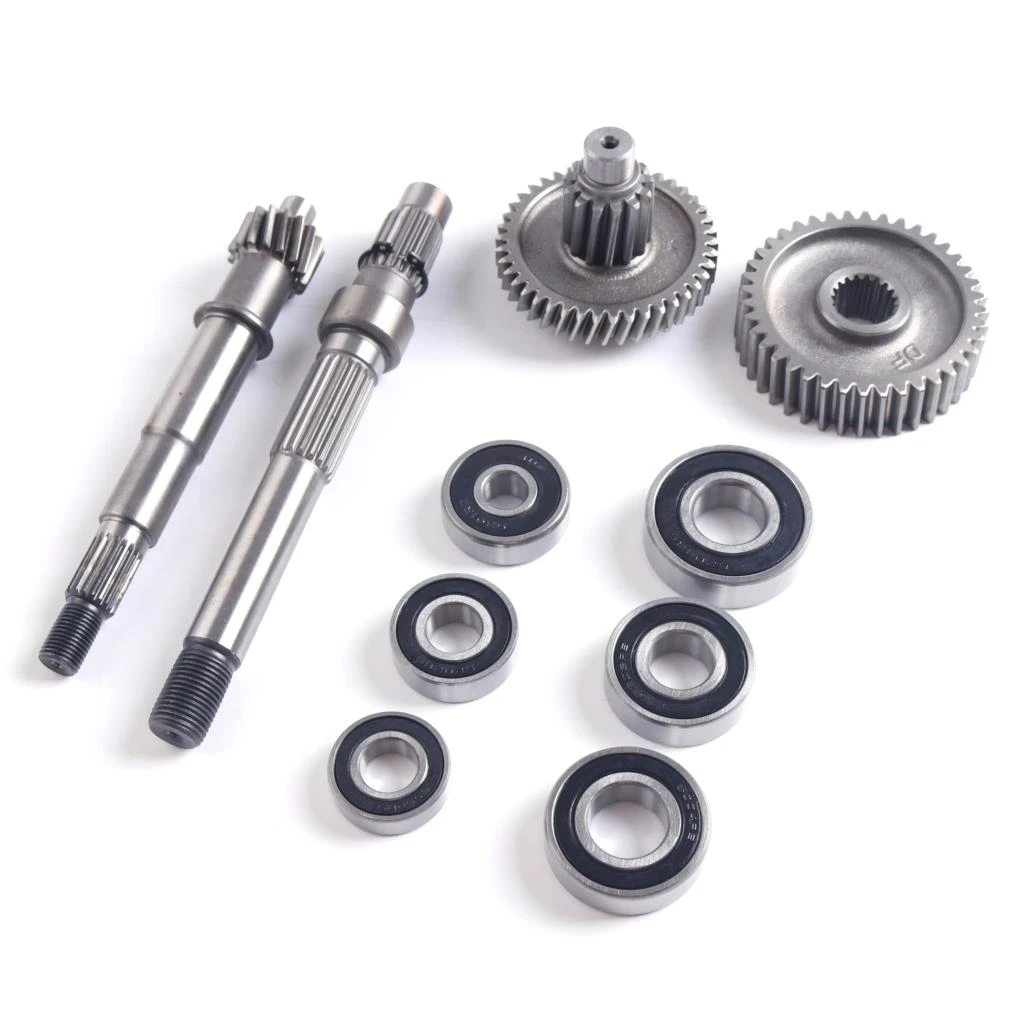

The gearbox is also where you need to change the gear oil to lubricate the parts periodically.
Here, we finish explaining the transmission system, the power is transmitted from Crankshaft to the Lubrication system.
For a 4-stroke GY6 engine, the lubrication uses a combination of pressure and splash. The oil pump below will pressurize the oil in the crankcase and deliver it to the surfaces of high-speed and high-load parts such as crankshafts, camshafts, and bearings. In the cylinder and cylinder head, oil passways let lubricating oil get through.
For parts that are difficult to use pressure lubrication, the lubrication is conducted by the engine oil splashed by the Crankshaft, gears, etc., or oil that falls from cylinder walls, timing gears, etc.
The location of the GY6 oil pump: In the crankcase, remove the magneto, the right crankcase cover, starting clutch, and the oil pump isolation plat. The Crankshaft drives the oil pump through the oil pump drive chain.
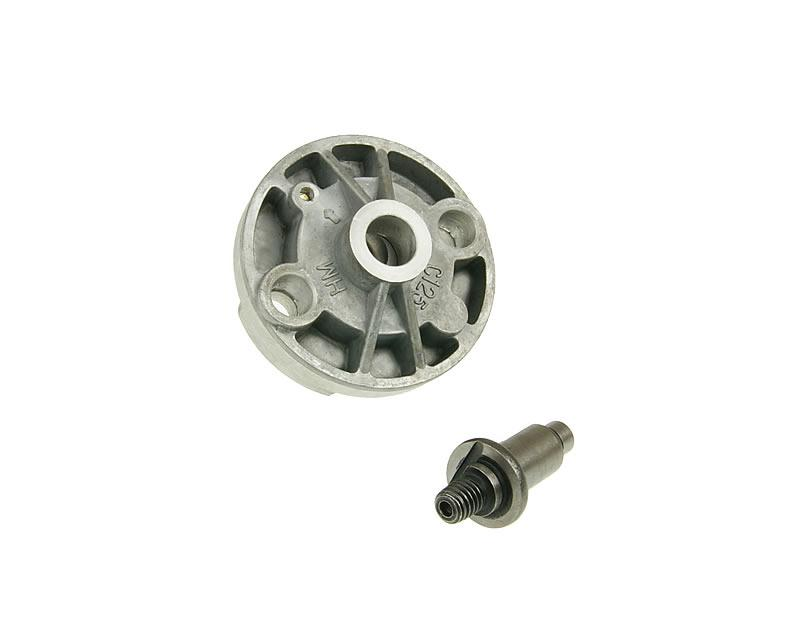

11. GY6 Start System
On some GY6 scooters, there are two ways you can start the scooter, kick start and electric start.
GY6 Kick Start
When you step on the starter lever, the power is transmitted to the starter shaft, and the gear on the starter shaft transmits the power to the front starter idler (the starter idler is fixed on the crankcase by the starter idler shaft), after that, the gear plate on the idler gear transmits power to the Crankshaft, then the Crankshaft rotates.
At the same time, the ignition switch should be pressed, the scooter should be ignited so that the engine starts to work.
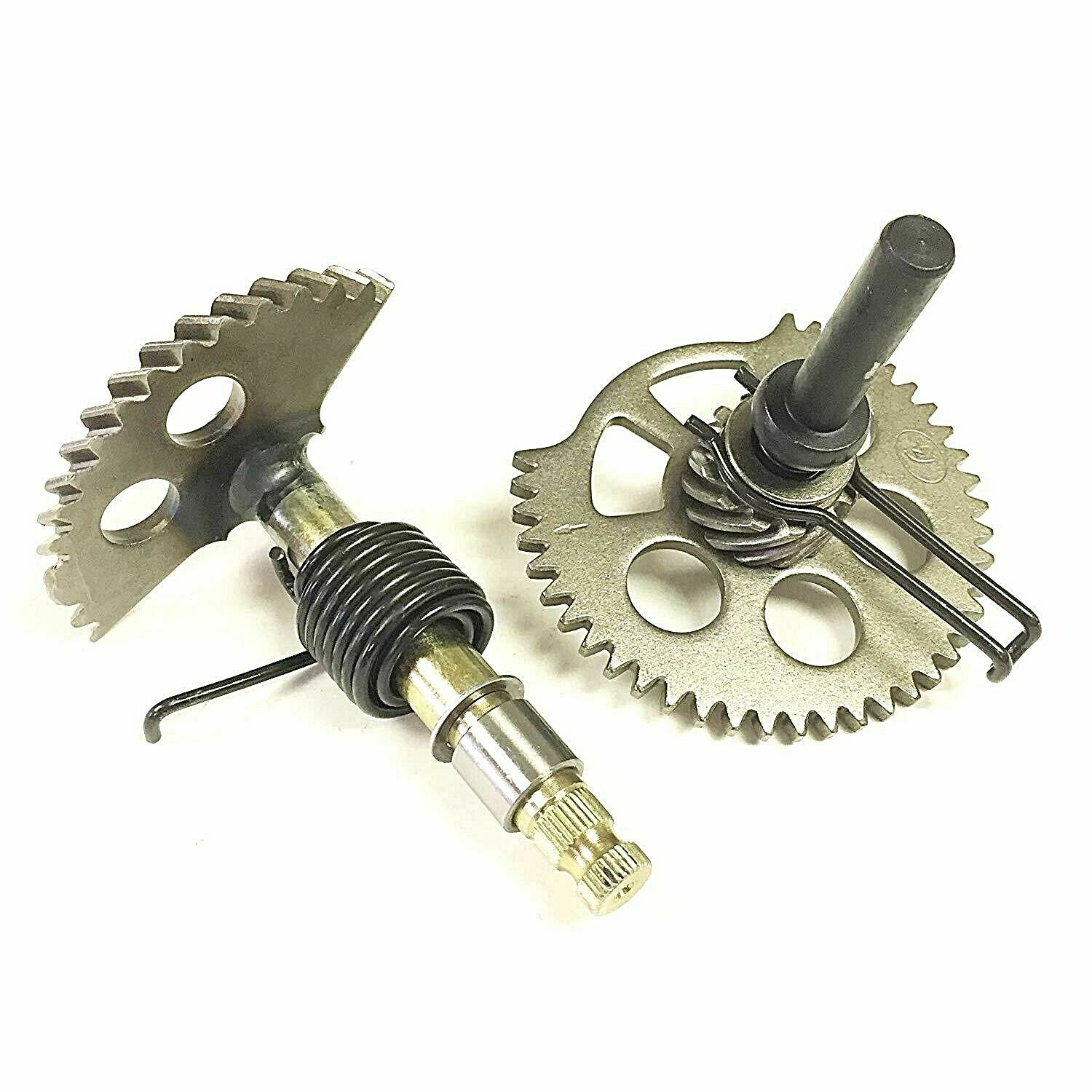

GY6 Electric start
The electric starting system is more common now and comprises a starting switch, a starting relay, a starting motor, a one-way starting clutch and a battery.
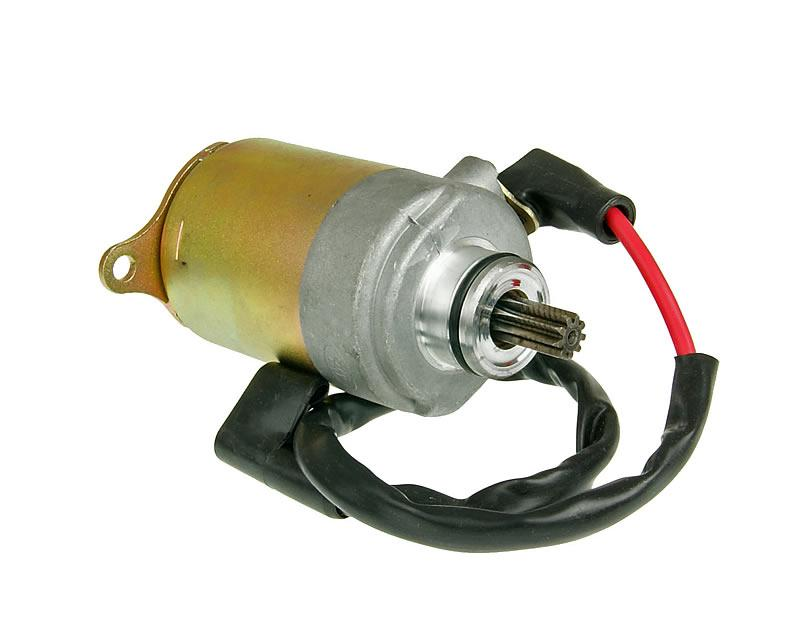

The whole process is like below:
Rotate the key to the On position —-> Press the start switch —-> the starting relay works (the circuit is connected) —–> the starting motor runs (the gear shaft rotates and drives the gears) ——> the one-way starting clutch works —–> Magneto rotor runs ——> Crankshaft rotation ——> Piston moves up and down to compress ——> Ignition is successful.
We have gone through most of the major points of the GY6 scooter and the engine, I hope this article is helpful for newbies and people who want to know better about their scooters.
Please share the website with others if you are inspired by it.

Excellent article! Very informative with great illustrations and videos!
Thank you, Micheal. I am really happy that the guide can help you know the GY6 engine better.